GNOME
Base GNOME packages for the full GNOME experience. Bundle with other packages to prevent package conflicts providing the same functionality.
TIP: Include any and all packages you want installed in a list to pacman. That way pacman will resolve package dependencies correctly and not install packages that would cause conflicts with other packages later on in the setup; e.g. the gnome group installs pulseaudio, but pulseaudio and pipewire (see below) are conflicting packages, meaning they can't both be installed at the same time prompting you to remove one or the other. Explicitly selected packages take precedence over packages auto-selected via dependencies.
The most basic installation of a GNOME desktop environment is easily done by installing the following package groups:
pacman -S gnome gnome-circle gnome-extra
gnome contians all the packages to run a basic GNOME desktop. gnome-circle contains additional applications from the "GNOME Circle" developer community. gnome-extra contains developer tools for GNOME applications and a few games.
Setting up display manager
Start GDM on boot
Start the GNOME Display Manager (GDM) on boot to be presented with a graphical login screen.
systemctl enable gdm
When using NVIDIA proprietary drivers
For the longest time NVIDIA only supported their EGLStreams interface for Wayland sessions. Despite GNOME having support for both EGLStreams and the more popular GBM interface, the GNOME Display Manager disables the Wayland session via a udev rule, if it detects the proprietary driver is in use, to prevent problems with the login screen not showing.
To force enable GNOME's Wayland session even with the proprietary NVIDIA driver installed, check the following files:
/etc/gdm/custom.conf: Make sure the lineWaylandEnable=falseis commented out (should be by default)/usr/lib/udev/rules.d/61-gdm.rules: Rename the file and create a symbolic link to/dev/nullln -s /dev/null /usr/lib/udev/rules.d/61-gdm.rules
Keep in mind that Wayland depends on Kernel Mode Setting to function properly, so it is necessary to include the appropriate kernel modules in the initramfs and setting the kernel commandline parameter to enable KMS support for the proprietary NVIDIA driver!
See Graphics Cards on how to set up early KMS with the proprietary NVIDIA driver.
Set Keymap for GDM
NOTE: Executing this command while chrooted into an installation will produce an error that the locale could not be found. Set after rebooting the system, press CTRL + ALT + F3 when GDM shows up (or any F-key between 2 and 7) to switch tty, log in via the command line and execute the command as root.
localectl set-x11-keymap de
See instructions at Plymouth page on how to set up Plymouth.
Misc additional packages
Additional packages you might want:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
gthumb |
Image viewer with simple editing capabilities |
lollypop |
Music player for GNOME |
seahorse |
Secrets manager (login credentials, SSH keys, GPG keys) |
fwupd |
Firmware update manager; allows UEFI capsule updates in GNOME Software if supported by firmware |
pacman -S gthumb lollypop seahorse fwupd
GNOME Keyring
Gnome Keyring is a useful tool for securely storing and managing passwords, SSH keys, and other sensitive information.
As gnome-keyring is already a member of the gnome package group, it should already be installed.
To manage the contents of gnome-keyring install seahorse:
pacman -S seahorse
SSH Keys
GNOME comes with GNOME Keyring as the component to store passwords and other secrets. It can act as a wrapper around ssh-agent and displays a GUI password entry dialog when you need to unlock an SSH key. This dialog also has a checkbox to remember the password, and will unlock the key automatically when you login to your GNOME session via your regular user password.
To utilize GNOME Keyring for storing SSH passphrases, install the gcr-4 package:
pacman -S gcr-4
Then, enable the gcr-ssh-agent.socket user unit:
systemctl --user enable --now gcr-ssh-agent.socker
This will create a socket file under $XDG_RUNTIME_DIR/gcr/ssh and set the $SSH_AUTH_SOCK environment variable, which ssh-agent uses to look for unlocked SSH keys and use them for authentication.
Uniform application styles
Qt applications
To make Qt/KDE applications fit in with the GNOME desktop you can install an Adwaita Qt theme and window decorations:
yay -S adwaita-qt{5,6}-git qadwaitadecorations-qt{5,6}
Then set the following environment variables in ~/.config/evironment.d/qt.conf:
QT_WAYLAND_DECORATION=adwaita
QT_STYLE_OVERRIDE=Adwaita-Dark
GTK3 applications
There is an Adwaita theme that brings GTK3 apps in line with the current LibAdwaita theme:
pacman -S adw-gtk-theme
Then open GNOME Tweaks and set the application theme for legacy applications to adw-gtk3 (or explicitly to adw-gtk3-dark if you notice apps that are not dark mode aware).
Flatpak apps
To apply Adwaita themes to Flatpak apps, install the following packages:
flatpak install org.gtk.Gtk3theme.adw-gtk3 org.gtk.Gtk3theme.adw-gtk3-dark
If you set the theme for legacy applications in GNOME Tweaks they will also be applied to Flatpak apps.
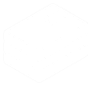
Firefox
Firefox can be customized to look like a GNOME native application by applying a GNOME Theme to it.
The simplest way to apply the theme is by installing Add Water, an application that allows you to install/remove the Firefox GNOME theme with a single click. It also allows to customize the GNOME theme with several options. It can auto-detect different versions of Firefox (repo package, Flatpak, Snap) as well as Firefox forks (Floorp, Cachy, LibreWolf).
flatpak install dev.qwery.AddWater
NOTE: When Firefox receives an update the theme can break in some ways. When this happens you can uninstall the theme temporarily or hold off on updating Firefox until an updated version of the theme becomes available.
Steam
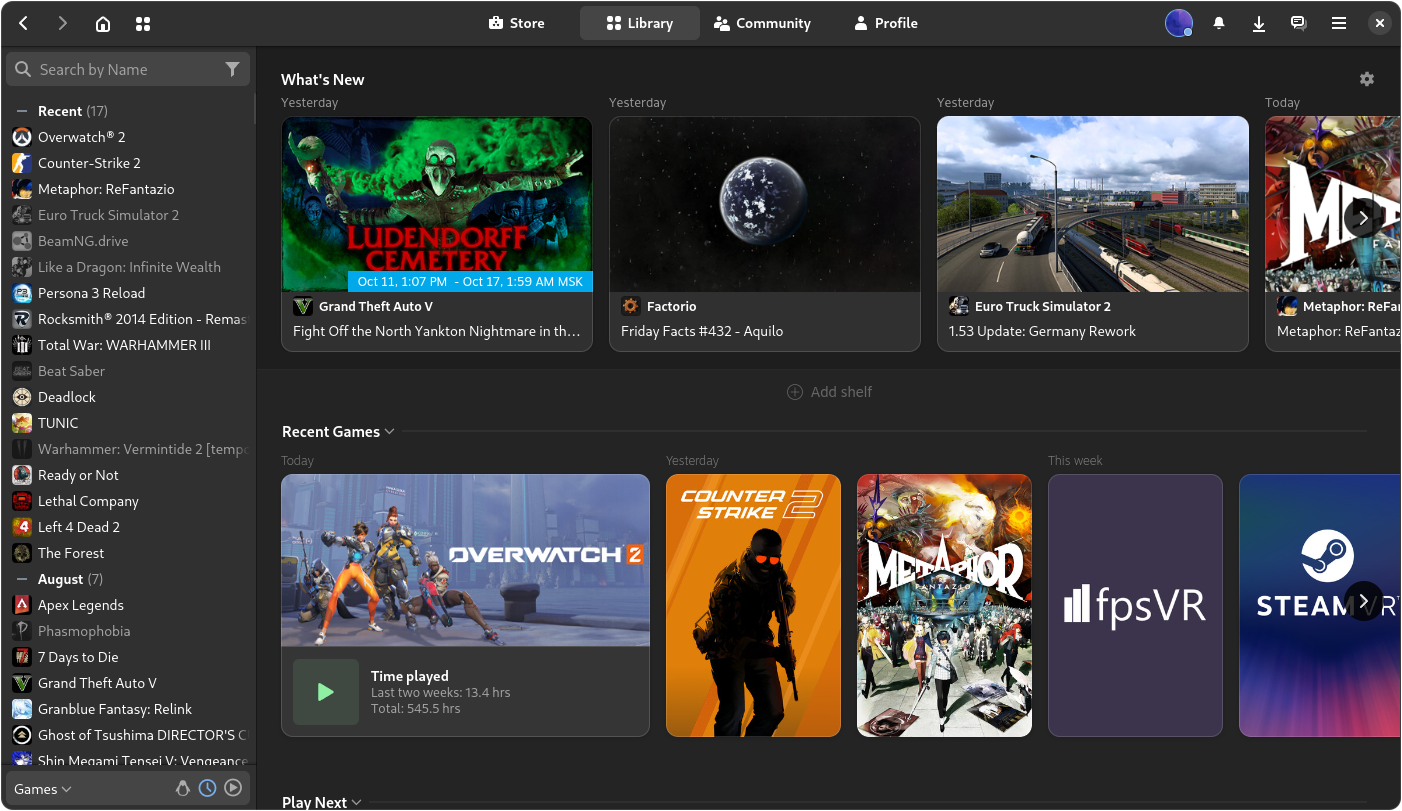
There is an Adwaita theme available for Steam to make it fit in with the rest of the GNOME desktop. An app is available that can install and manage the theme for you:
flatpak install io.github.Foldex.AdwSteamGtk
Remove potentially unwanted packages
GNOME Dev Tools
pacman -Rsc gnome-{builder,devel-docs,multi-writer,terminal} accerciser d-spy devhelp glade sysprof
User Software
pacman -Rsc gnome-{notes,recipes,sound-recorder} polari
Games
pacman -Rsc gnome-{2048,chess,games,klotski,mahjongg,mines,nibbles,sudoku,taquin,tetravex} hitori iagno lightsoff quadrapassel tali
Replace repo packages with Flatpaks
If you wish to use the Flatpak versions of packages that the GNOME desktop team maintains themselves, you can uninstall the packages that are available as Flatpak in GNOME Software.
Remove
TIP: Put substrings of package names between curly brackets { } so the shell substitutes the values, e.g. gnome-{calculator,calendar,characters,clocks} is interpreted as if you typed gnome-calculator gnome-calendar gnome-characters gnome-clocks. Nesting also works!
Packages part of the gnome package group:
pacman -Rn gnome-{calculator,calendar,characters,clocks,connections,contacts,font-viewer,logs,maps,music,text-editor,weather} \
epiphany evince loupe simple-scan snapshot sushi totem decibels
Packages part of the gnome-extra package group:
pacman -Rn chatty d-spy dconf-editor devhelp endeavour file-roller ghex gnome-{boxes,builder,calls,chess,mahjongg,mines,nibbles,robots,sound-recorder,sudoku,tweaks} lightsoff quadrapassel swell-foop sysprof
Reinstall
Install the core GNOME apps as Flatpaks:
NOTE: Some of the repo packages of the gnome-extra group have been discontinued by GNOME. The following Flatpak selections replaces these with actively developed alternatives.
flatpak install flathub org.gnome.{Calculator,Calendar,Calls,Snapshot,Characters,clocks,Connections,Contacts,SimpleScan,Evince,Extensions,font-viewer,Loupe,Decibels,Logs,Maps,Music,NautilusPreviewer,TextEditor,Showtime,Weather,Epiphany}
Selection of Flatpaks previously from the gnome-extra package group:
flatpak install flathub org.gnome.{Evolution,Geary,GHex,Glade,Boxes,seahorse.Application,World.Iotas} ca.desrt.dconf-editor io.github.alainm23.planify page.kramo.Cartridges page.tesk.Refine com.mattjakeman.ExtensionManager io.gitlab.adhami3310.Impression
For a list of additional packages, see GNOME Flatpaks.